Global Conversations: Nature, Place, and Education
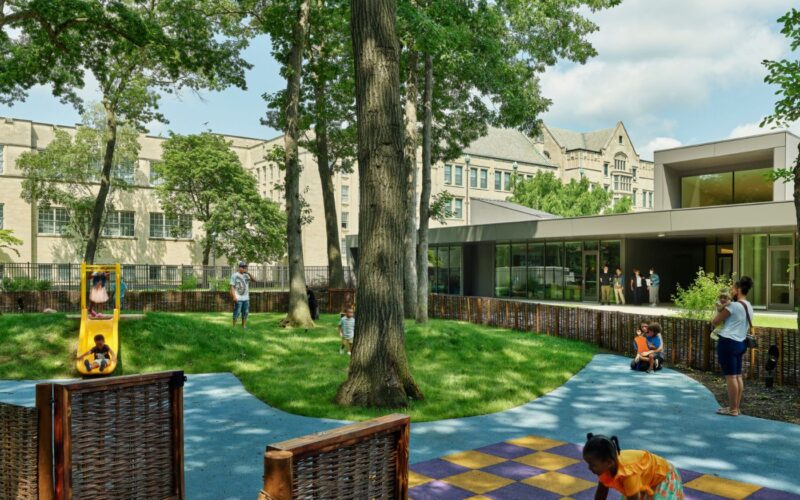
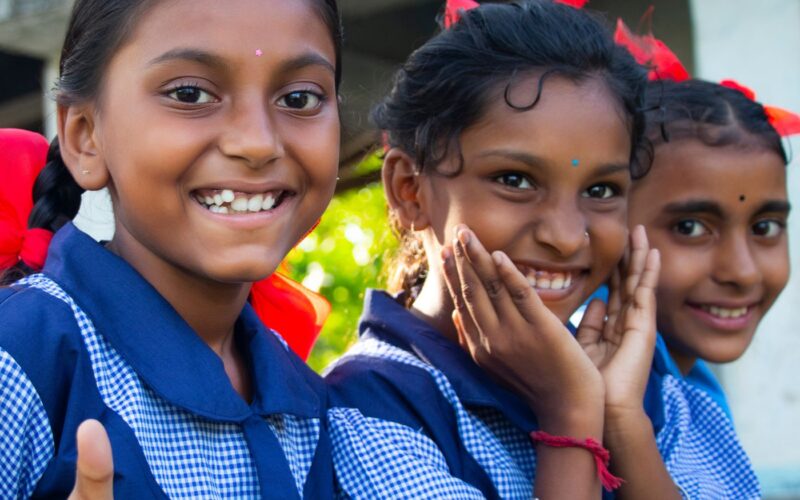
We share brief presentations from the first of the “Saturday Salons” that Ethical Schools is sponsoring with three international partners. Juan Mora of the Center for Artistry and Scholarship and Ramji Raghavan of Agastya International Foundation talk about how educators and communities can cultivate awareness of and relationship to the natural world.
Learn more and register for the next salon at globalconversations.net
Read More